elisa test examples|different types of elisa test : distributing An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, also called ELISA or EIA, is a test that detects and . The U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) Manufacturing and Industrial Technology Division (ManTech) is collaborating with Boeing and Indiana-based machinery manufacturer Thermwood to produce.
{plog:ftitle_list}
The autoclave is what keeps you safe and keeps your piercing from contamination. Without this machine, body piercing as we know it would be virtually impossible without causing infections.
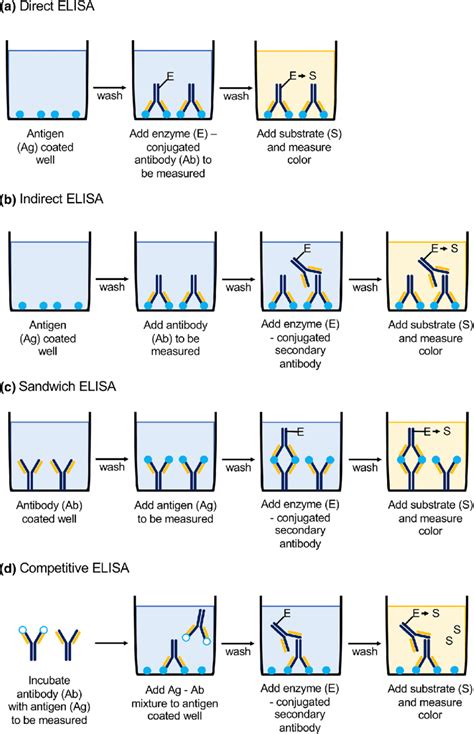
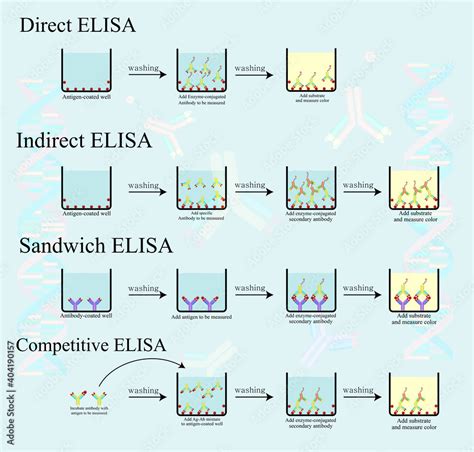
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, also called ELISA or EIA, is a test that detects and .The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (/ ɪ ˈ l aɪ z ə /, / ˌ iː ˈ l aɪ z ə /) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. [1] The assay is a solid-phase type of enzyme .Examples of the uses of an ELISA test include diagnosing infections such as HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) and some allergic diseases like food allergies and experimental investigations to identify compounds (antigens from a cell lysate in a wide array of organisms). ELISA tests are also known as immunosorbent assay or enzyme immunoassay . What is ELISA? The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an antibody-based technique for the detection and quantification of target analytes in solution. The targets are typically proteins, for example, cytokines, chemokines, immunoglobulins, hormones, and other biomarkers. ELISA setups include direct/indirect (antigen first), competitive, and sandwich .
An ELISA test has few risks because the test itself is performed on your blood sample in a lab. The risks come from the process of getting your blood sample drawn. Some potential risks of getting .For direct detection, test sample and enzyme-conjugated control antigen are added simultaneously, and a stronger signal will indicate that more control antigen is bound, reflecting lower analyte concentration in the sample. For indirect detection, test sample, enzyme-conjugated control antigen and capture antibody are added simultaneously.
A blood sample is needed. Most of the time, blood is drawn from a vein located on the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. The sample is sent to a laboratory where the targeted antibody or antigen is linked to a specific enzyme. If the target substance is in the sample, the test solution turns a different color.Why is an ELISA test so sensitive? ELISAs tend to be the most sensitive immunoassays due to the binding characteristics of the antibodies and the amplification or different read-out systems used. Sample volumes can also be adjusted when you have a very low abundant protein.
level 3 hard body impact test
antigen in a sample . May be used to test various sample types: serum, plasma, cellular and tissue extracts, urine, and saliva, among others. These are the general ELISA advantages and disadvantages . There are other advantages and disadvantages depending on the type of ELISA used as explained in the next section. How Is the ELISA Test Performed? A blood sample is needed. Most of the time, blood is drawn from a vein located on the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. The sample is sent to a laboratory where the targeted antibody or antigen is linked to a specific enzyme. If the target substance is in the sample, the test solution turns a . One example is the TORCH test that allows doctors to screen pregnant women or newborns for infection by an array of viruses and other pathogens (Toxoplasma, other viruses, rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex). In-home pregnancy tests are another widely used example of a lateral flow test (Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)).Fig. 5. Competition ELISA. An example of a competition ELISA to test for antigen based on the direct detection method is shown in Figure 5 . Remove liquid and wash plate Remove liquid and wash plate Remove liquid and wash plate Remove liquid and wash plate In this example the antigen concentration in the sample was low. The antibodies bound the
biological samples . Some examples include : diagnosis of HIV infection, pregnancy tests, and measurement of cytokines or soluble receptors in cell supernatant or serum . ELISA assays are generally carried out in 96 well plates, allowing multiple samples to be .Fig: Detection Strategies of ELISA. Types: ELISA tests are categorized into three categories based on the methods applied to bind antigen and antibodies, namely: Indirect and Direct ELISA. The crucial step is to immobilize the antigen of interest, which can be done directly on the test plate or indirectly via a capture antibody linked to the plate.ELISA is one of the easiest blood tests that can be carried out. It is rapid, quick and requires a blood sample of the patient. The entire procedure of ELISA is mentioned below. . If HCG is absent in the test sample, then only the linked enzyme binds to the solid surface. The more the substance of interest is present, the more reaction takes .Advantages of ELISA Test. ELISA is the qualitative and quantitative assay, i.e. it not only detects the presence of the analyte but also detects the concentration or quantity of the analyte. It can screen a large number of samples in a single take. ELISA can be easily automated. Disadvantages of ELISA Test
ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) tests are widely employed laboratory techniques used to detect and quantify proteins, antibodies, and hormones in a sample, making them crucial tools in diagnostics and research. This highly sensitive assay leverages an enzyme-linked antigen or antibody to produce a measurable color change, indicating the presence and concentration .
Originally described by Engvall and Perlmann (1971), the method enables analysis of protein samples immobilized in microplate wells using specific antibodies. ELISAs are typically performed in 96-well or 384-well polystyrene .
What Does ELISA Do? ELISAs deliver a simple, robust, and cost-effective method to analyze and quantify one or more antigens from a variety of sample types, such as cell lysate, tissue lysate, or serum. ELISA is a popular technique for research and diagnostic samples and can be used as both a single sample test or high throughput method for . ELISA test kits and the knowledge of the various sorts of ELISA test kits are crucial aspects of contemporary scientific exploration and healthcare progress. In the domain of ELISA applications, the importance of this method cannot be emphasized enough. In medical investigation, ELISA performs a central function in disclosing the complexities .Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an immunological technique extensively used in research and clinical laboratory settings to quantitatively identify a specific protein (i.e., the antigen or biomarker) in a biological matrix while relying on the principle of the specific binding interaction between the antigen and the antibody against the antigen of interest . An enzyme immunoassay (EIA) or an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a blood or urine analysis that can help diagnose many infections and inflammatory conditions. This is a simple test that does not cause side effects. Your EIA can help in diagnosing the cause of your symptoms and is used to guide your therapy.
One variation in ELISA can be a constant target antigen coated onto the plate, but with unknown antibodies from patient samples. The ANA test serves as an appropriate example in that the purpose is to detect specific antibody in the patient’s blood stream rather than the target of those antibodies . As such, the plate-immobilized antigen .
How the Test is Performed. A blood sample is needed. Most of the time, blood is drawn from a vein located on the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand.. The sample is sent to a laboratory where the targeted antibody or antigen is linked to a specific enzyme.If the target substance is in the sample, the test solution turns a different color. The Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is a biomolecular technique that utilizes the specificity of an antibody, as well as the sensitivity of enzyme assays, to detect and quantify . Enzyme immunoassays (EIAs) use the catalytic properties of enzymes to detect and quantify immunologic reactions. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a heterogeneous EIA technique used in clinical analyses. In this type of assay, one of the reaction components is nonspecifically adsorbed or .
Fold-change may be determined by using a baseline sample of serum antibodies to compare a sample of serum antibodies in response to an infection. Qualitative ELISA Test Results. Qualitative analysis of ELISA determines the presence or absence of the target analyte and is used when research calls for just a positive or negative signal.
ELISA (Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay) is an immunologic technique used to detect the presence and concentration of an antigen or antibody in a sample. The power of an ELISA is based on the extreme specificity of the antigen-antibody interaction. ELISAs have wide-ranging applications, especially as medical diagnostic tools. Figure 1. ELISA .
types of elisa diagram
However, for practical purposes, I prefer to autoclave a 60 % (v/v) glycerol solution, prepared by weighing glycerol to avoid problems due to glycerol sticking to volumetric devices, because at .
elisa test examples|different types of elisa test